Diesel injection systems can be divided into two categories:
The first is based on the design of the combustion chamber.
Combustion chamber designs vary from one engine to another. In general, the design can be evaluated based on the ease or difficulty of implementing the design during engine production, the design's ability to achieve the highest combustion efficiency to produce the greatest possible amount of power, fuel consumption, and maintainability.
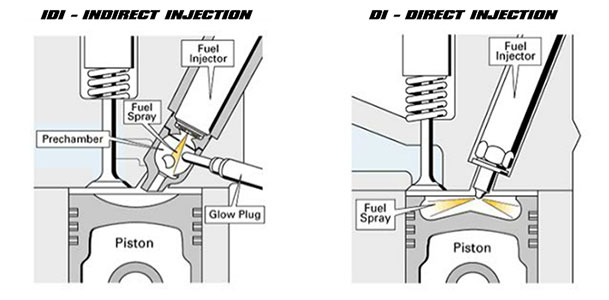
In general, engines can be divided into direct injection and indirect injection.
In direct injection, fuel is injected onto the surface above the piston's surface. Some engine pistons are designed to contain a combustion chamber to increase the efficiency of the fuel combustion process. In indirect injection, sub-combustion chambers are designed in the cylinder head. Combustion occurs in two stages: first, in the sub-chamber, then the main chamber. Diesel is injected into the sub-chamber.
Two types can be distinguished: In direct injection, there is a single chamber above or within the piston's surface, into which injection occurs. In indirect injection, there are two chambers, with injection occurring in the sub-chamber and combustion occurring in the main chamber.